Installation
Frigate is a Docker container that can be run on any Docker host including as a HassOS Addon. Note that a Home Assistant Addon is not the same thing as the integration. The integration is required to integrate Frigate into Home Assistant.
If you already have Frigate installed as a Home Assistant addon, check out the getting started guide to configure Frigate.
Dependencies
MQTT broker (optional) - An MQTT broker is optional with Frigate, but is required for the Home Assistant integration. If using Home Assistant, Frigate and Home Assistant must be connected to the same MQTT broker.
Preparing your hardware
Operating System
Frigate runs best with Docker installed on bare metal Debian-based distributions. For ideal performance, Frigate needs low overhead access to underlying hardware for the Coral and GPU devices. Running Frigate in a VM on top of Proxmox, ESXi, Virtualbox, etc. is not recommended though some users have had success with Proxmox.
Windows is not officially supported, but some users have had success getting it to run under WSL or Virtualbox. Getting the GPU and/or Coral devices properly passed to Frigate may be difficult or impossible. Search previous discussions or issues for help.
Storage
Frigate uses the following locations for read/write operations in the container. Docker volume mappings can be used to map these to any location on your host machine.
/config: Used to store the Frigate config file and sqlite database. You will also see a few files alongside the database file while Frigate is running./media/frigate/clips: Used for snapshot storage. In the future, it will likely be renamed fromclipstosnapshots. The file structure here cannot be modified and isn't intended to be browsed or managed manually./media/frigate/recordings: Internal system storage for recording segments. The file structure here cannot be modified and isn't intended to be browsed or managed manually./media/frigate/exports: Storage for clips and timelapses that have been exported via the WebUI or API./tmp/cache: Cache location for recording segments. Initial recordings are written here before being checked and converted to mp4 and moved to the recordings folder. Segments generated via theclip.mp4endpoints are also concatenated and processed here. It is recommended to use atmpfsmount for this./dev/shm: Internal cache for raw decoded frames in shared memory. It is not recommended to modify this directory or map it with docker. The minimum size is impacted by theshm-sizecalculations below.
Ports
The following ports are used by Frigate and can be mapped via docker as required.
| Port | Description |
|---|---|
8971 | Authenticated UI and API access without TLS. Reverse proxies should use this port. |
5000 | Internal unauthenticated UI and API access. Access to this port should be limited. Intended to be used within the docker network for services that integrate with Frigate. |
8554 | RTSP restreaming. By default, these streams are unauthenticated. Authentication can be configured in go2rtc section of config. |
8555 | WebRTC connections for low latency live views. |
Common docker compose storage configurations
Writing to a local disk or external USB drive:
services:
frigate:
...
volumes:
- /path/to/your/config:/config
- /path/to/your/storage:/media/frigate
- type: tmpfs # Optional: 1GB of memory, reduces SSD/SD Card wear
target: /tmp/cache
tmpfs:
size: 1000000000
...
Users of the Snapcraft build of Docker cannot use storage locations outside your $HOME folder.
Calculating required shm-size
Frigate utilizes shared memory to store frames during processing. The default shm-size provided by Docker is 64MB.
The default shm size of 128MB is fine for setups with 2 cameras detecting at 720p. If Frigate is exiting with "Bus error" messages, it is likely because you have too many high resolution cameras and you need to specify a higher shm size, using --shm-size (or service.shm_size in docker-compose).
The Frigate container also stores logs in shm, which can take up to 40MB, so make sure to take this into account in your math as well.
You can calculate the minimum shm size for each camera with the following formula using the resolution specified for detect:
# Replace <width> and <height>
$ python -c 'print("{:.2f}MB".format((<width> * <height> * 1.5 * 20 + 270480) / 1048576))'
# Example for 1280x720, including logs
$ python -c 'print("{:.2f}MB".format((1280 * 720 * 1.5 * 20 + 270480) / 1048576)) + 40'
46.63MB
# Example for eight cameras detecting at 1280x720, including logs
$ python -c 'print("{:.2f}MB".format(((1280 * 720 * 1.5 * 20 + 270480) / 1048576) * 8 + 40))'
253MB
The shm size cannot be set per container for Home Assistant add-ons. However, this is probably not required since by default Home Assistant Supervisor allocates /dev/shm with half the size of your total memory. If your machine has 8GB of memory, chances are that Frigate will have access to up to 4GB without any additional configuration.
Raspberry Pi 3/4
By default, the Raspberry Pi limits the amount of memory available to the GPU. In order to use ffmpeg hardware acceleration, you must increase the available memory by setting gpu_mem to the maximum recommended value in config.txt as described in the official docs.
Additionally, the USB Coral draws a considerable amount of power. If using any other USB devices such as an SSD, you will experience instability due to the Pi not providing enough power to USB devices. You will need to purchase an external USB hub with it's own power supply. Some have reported success with this (affiliate link).
Hailo-8L
The Hailo-8L is an M.2 card typically connected to a carrier board for PCIe, which then connects to the Raspberry Pi 5 as part of the AI Kit. However, it can also be used on other boards equipped with an M.2 M key edge connector.
Installation
For Raspberry Pi 5 users with the AI Kit, installation is straightforward. Simply follow this guide to install the driver and software.
For other installations, follow these steps for installation:
- Install the driver from the Hailo GitHub repository. A convenient script for Linux is available to clone the repository, build the driver, and install it.
- Copy or download this script.
- Ensure it has execution permissions with
sudo chmod +x user_installation.sh - Run the script with
./user_installation.sh
Setup
To set up Frigate, follow the default installation instructions, but use a Docker image with the -h8l suffix, for example: ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable-h8l
Next, grant Docker permissions to access your hardware by adding the following lines to your docker-compose.yml file:
devices:
- /dev/hailo0
If you are using docker run, add this option to your command --device /dev/hailo0
Configuration
Finally, configure hardware object detection to complete the setup.
Rockchip platform
Make sure that you use a linux distribution that comes with the rockchip BSP kernel 5.10 or 6.1 and necessary drivers (especially rkvdec2 and rknpu). To check, enter the following commands:
$ uname -r
5.10.xxx-rockchip # or 6.1.xxx; the -rockchip suffix is important
$ ls /dev/dri
by-path card0 card1 renderD128 renderD129 # should list renderD128 (VPU) and renderD129 (NPU)
$ sudo cat /sys/kernel/debug/rknpu/version
RKNPU driver: v0.9.2 # or later version
I recommend Joshua Riek's Ubuntu for Rockchip, if your board is supported.
Setup
Follow Frigate's default installation instructions, but use a docker image with -rk suffix for example ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable-rk.
Next, you need to grant docker permissions to access your hardware:
- During the configuration process, you should run docker in privileged mode to avoid any errors due to insufficient permissions. To do so, add
privileged: trueto yourdocker-compose.ymlfile or the--privilegedflag to your docker run command. - After everything works, you should only grant necessary permissions to increase security. Disable the privileged mode and add the lines below to your
docker-compose.ymlfile:
security_opt:
- apparmor=unconfined
- systempaths=unconfined
devices:
- /dev/dri
- /dev/dma_heap
- /dev/rga
- /dev/mpp_service
or add these options to your docker run command:
--security-opt systempaths=unconfined \
--security-opt apparmor=unconfined \
--device /dev/dri \
--device /dev/dma_heap \
--device /dev/rga \
--device /dev/mpp_service
Configuration
Next, you should configure hardware object detection and hardware video processing.
Docker
Running in Docker with compose is the recommended install method.
version: "3.9"
services:
frigate:
container_name: frigate
privileged: true # this may not be necessary for all setups
restart: unless-stopped
stop_grace_period: 30s # allow enough time to shut down the various services
image: ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable
shm_size: "512mb" # update for your cameras based on calculation above
devices:
- /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb # Passes the USB Coral, needs to be modified for other versions
- /dev/apex_0:/dev/apex_0 # Passes a PCIe Coral, follow driver instructions here https://coral.ai/docs/m2/get-started/#2a-on-linux
- /dev/video11:/dev/video11 # For Raspberry Pi 4B
- /dev/dri/renderD128:/dev/dri/renderD128 # For intel hwaccel, needs to be updated for your hardware
volumes:
- /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
- /path/to/your/config:/config
- /path/to/your/storage:/media/frigate
- type: tmpfs # Optional: 1GB of memory, reduces SSD/SD Card wear
target: /tmp/cache
tmpfs:
size: 1000000000
ports:
- "8971:8971"
# - "5000:5000" # Internal unauthenticated access. Expose carefully.
- "8554:8554" # RTSP feeds
- "8555:8555/tcp" # WebRTC over tcp
- "8555:8555/udp" # WebRTC over udp
environment:
FRIGATE_RTSP_PASSWORD: "password"
If you can't use docker compose, you can run the container with something similar to this:
docker run -d \
--name frigate \
--restart=unless-stopped \
--stop-timeout 30 \
--mount type=tmpfs,target=/tmp/cache,tmpfs-size=1000000000 \
--device /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb \
--device /dev/dri/renderD128 \
--shm-size=64m \
-v /path/to/your/storage:/media/frigate \
-v /path/to/your/config:/config \
-v /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro \
-e FRIGATE_RTSP_PASSWORD='password' \
-p 8971:8971 \
-p 8554:8554 \
-p 8555:8555/tcp \
-p 8555:8555/udp \
ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable
The official docker image tags for the current stable version are:
stable- Standard Frigate build for amd64 & RPi Optimized Frigate build for arm64stable-standard-arm64- Standard Frigate build for arm64stable-tensorrt- Frigate build specific for amd64 devices running an nvidia GPU
The community supported docker image tags for the current stable version are:
stable-tensorrt-jp5- Frigate build optimized for nvidia Jetson devices running Jetpack 5stable-tensorrt-jp4- Frigate build optimized for nvidia Jetson devices running Jetpack 4.6stable-rk- Frigate build for SBCs with Rockchip SoCstable-rocm- Frigate build for AMD GPUsstable-h8l- Frigate build for the Hailo-8L M.2 PICe Raspberry Pi 5 hat
Home Assistant Addon
As of HomeAssistant OS 10.2 and Core 2023.6 defining separate network storage for media is supported.
There are important limitations in Home Assistant Operating System to be aware of:
- Separate local storage for media is not yet supported by Home Assistant
- AMD GPUs are not supported because HA OS does not include the mesa driver.
- Nvidia GPUs are not supported because addons do not support the nvidia runtime.
See the network storage guide for instructions to setup network storage for frigate.
HassOS users can install via the addon repository.
- Navigate to Supervisor > Add-on Store > Repositories
- Add https://github.com/blakeblackshear/frigate-hass-addons
- Install your desired Frigate NVR Addon and navigate to it's page
- Setup your network configuration in the
Configurationtab - (not for proxy addon) Create the file
frigate.yamlin yourconfigdirectory with your detailed Frigate configuration - Start the addon container
- (not for proxy addon) If you are using hardware acceleration for ffmpeg, you may need to disable "Protection mode"
There are several versions of the addon available:
| Addon Version | Description |
|---|---|
| Frigate NVR | Current release with protection mode on |
| Frigate NVR (Full Access) | Current release with the option to disable protection mode |
| Frigate NVR Beta | Beta release with protection mode on |
| Frigate NVR Beta (Full Access) | Beta release with the option to disable protection mode |
Kubernetes
Use the helm chart.
Unraid
Many people have powerful enough NAS devices or home servers to also run docker. There is a Unraid Community App. To install make sure you have the community app plugin here. Then search for "Frigate" in the apps section within Unraid - you can see the online store here
Proxmox
According to Proxmox documentation it is recommended that you run application containers like Frigate inside a Proxmox QEMU VM. This will give you all the advantages of application containerization, while also providing the benefits that VMs offer, such as strong isolation from the host and the ability to live-migrate, which otherwise isn’t possible with containers.
If you choose to run Frigate via LXC in Proxmox the setup can be complex so be prepared to read the Proxmox and LXC documentation, Frigate does not officially support running inside of an LXC.
Suggestions include:
- For Intel-based hardware acceleration, to allow access to the
/dev/dri/renderD128device with major number 226 and minor number 128, add the following lines to the/etc/pve/lxc/<id>.confLXC configuration:lxc.cgroup2.devices.allow: c 226:128 rwmlxc.mount.entry: /dev/dri/renderD128 dev/dri/renderD128 none bind,optional,create=file
- The LXC configuration will likely also need
features: fuse=1,nesting=1. This allows running a Docker container in an LXC container (nesting) and prevents duplicated files and wasted storage (fuse). - Successfully passing hardware devices through multiple levels of containerization (LXC then Docker) can be difficult. Many people make devices like
/dev/dri/renderD128world-readable in the host or run Frigate in a privileged LXC container. - The virtualization layer often introduces a sizable amount of overhead for communication with Coral devices, but not in all circumstances.
See the Proxmox LXC discussion for more general information.
ESXi
For details on running Frigate using ESXi, please see the instructions here.
If you're running Frigate on a rack mounted server and want to passthrough the Google Coral, read this.
Synology NAS on DSM 7
These settings were tested on DSM 7.1.1-42962 Update 4
General:
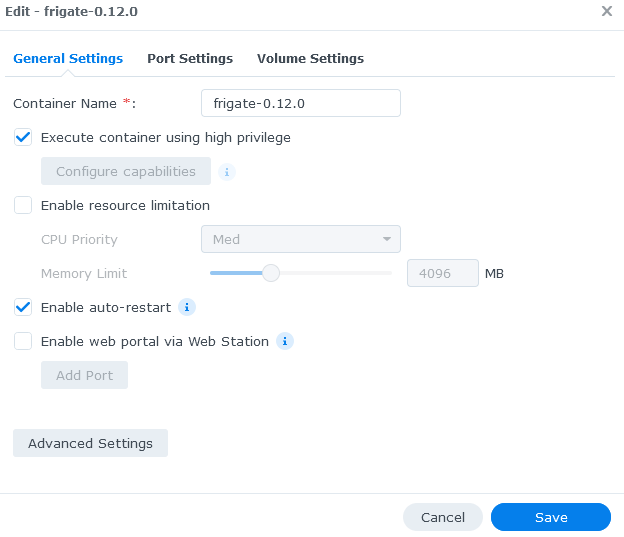
The Execute container using high privilege option needs to be enabled in order to give the frigate container the elevated privileges it may need.
The Enable auto-restart option can be enabled if you want the container to automatically restart whenever it improperly shuts down due to an error.
Advanced Settings:
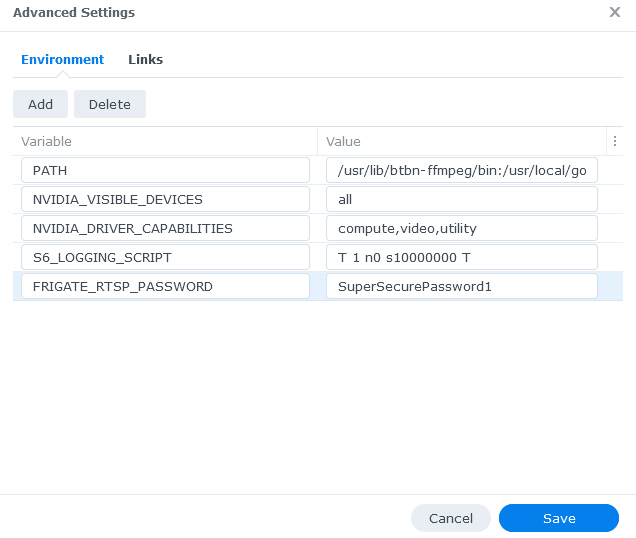
If you want to use the password template feature, you should add the "FRIGATE_RTSP_PASSWORD" environment variable and set it to your preferred password under advanced settings. The rest of the environment variables should be left as default for now.
Port Settings:
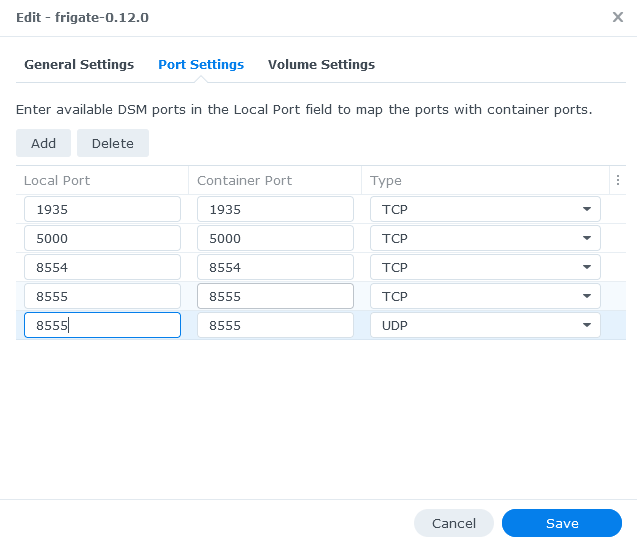
The network mode should be set to bridge. You need to map the default frigate container ports to your local Synology NAS ports that you want to use to access Frigate.
There may be other services running on your NAS that are using the same ports that frigate uses. In that instance you can set the ports to auto or a specific port.
Volume Settings:
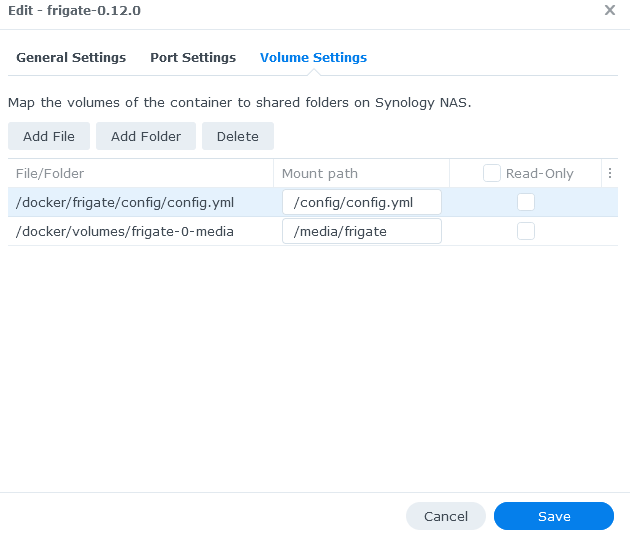
You need to configure 2 paths:
- The location of your config directory which will be different depending on your NAS folder structure e.g.
/docker/frigate/configwill mount to/configwithin the container. - The location on your NAS where the recordings will be saved this needs to be a folder e.g.
/docker/volumes/frigate-0-media
QNAP NAS
These instructions were tested on a QNAP with an Intel J3455 CPU and 16G RAM, running QTS 4.5.4.2117.
QNAP has a graphic tool named Container Station to install and manage docker containers. However, there are two limitations with Container Station that make it unsuitable to install Frigate:
- Container Station does not incorporate GitHub Container Registry (ghcr), which hosts Frigate docker image version 0.12.0 and above.
- Container Station uses default 64 Mb shared memory size (shm-size), and does not have a mechanism to adjust it. Frigate requires a larger shm-size to be able to work properly with more than two high resolution cameras.
Because of above limitations, the installation has to be done from command line. Here are the steps:
Preparation
- Install Container Station from QNAP App Center if it is not installed.
- Enable ssh on your QNAP (please do an Internet search on how to do this).
- Prepare Frigate config file, name it
config.yml. - Calculate shared memory size according to documentation.
- Find your time zone value from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_tz_database_time_zones
- ssh to QNAP.
Installation
Run the following commands to install Frigate (using stable version as example):
# Download Frigate image
docker pull ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable
# Create directory to host Frigate config file on QNAP file system.
# E.g., you can choose to create it under /share/Container.
mkdir -p /share/Container/frigate/config
# Copy the config file prepared in step 2 into the newly created config directory.
cp path/to/your/config/file /share/Container/frigate/config
# Create directory to host Frigate media files on QNAP file system.
# (if you have a surveillance disk, create media directory on the surveillance disk.
# Example command assumes share_vol2 is the surveillance drive
mkdir -p /share/share_vol2/frigate/media
# Create Frigate docker container. Replace shm-size value with the value from preparation step 3.
# Also replace the time zone value for 'TZ' in the sample command.
# Example command will create a docker container that uses at most 2 CPUs and 4G RAM.
# You may need to add "--env=LIBVA_DRIVER_NAME=i965 \" to the following docker run command if you
# have certain CPU (e.g., J4125). See https://docs.frigate.video/configuration/hardware_acceleration.
docker run \
--name=frigate \
--shm-size=256m \
--restart=unless-stopped \
--env=TZ=America/New_York \
--volume=/share/Container/frigate/config:/config:rw \
--volume=/share/share_vol2/frigate/media:/media/frigate:rw \
--network=bridge \
--privileged \
--workdir=/opt/frigate \
-p 8971:8971 \
-p 8554:8554 \
-p 8555:8555 \
-p 8555:8555/udp \
--label='com.qnap.qcs.network.mode=nat' \
--label='com.qnap.qcs.gpu=False' \
--memory="4g" \
--cpus="2" \
--detach=true \
-t \
ghcr.io/blakeblackshear/frigate:stable
Log into QNAP, open Container Station. Frigate docker container should be listed under 'Overview' and running. Visit Frigate Web UI by clicking Frigate docker, and then clicking the URL shown at the top of the detail page.